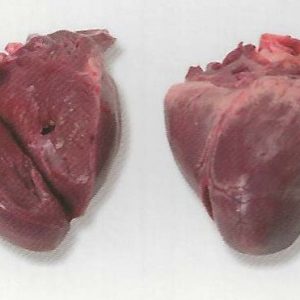
Frozen buffalo heart nutrition may not be the first thing that comes to mind when considering healthy food options, but this nutrient-packed organ meat deserves a spot in your diet. Whether you’re an athlete looking for high-quality protein or someone seeking a low-fat, nutrient-dense food, frozen buffalo heart is a hidden gem.
What is Frozen Buffalo Heart?
The buffalo heart is a lean, nutrient-dense organ meat from the water buffalo. When frozen, it retains its nutritional properties, making it convenient and long-lasting for storage.
Why Consider Frozen Buffalo Heart for Nutrition?
Organ meats like buffalo heart have been staples in traditional diets for centuries due to their rich nutrient content. Unlike muscle meat, organ meats are often higher in vitamins and minerals, offering a powerhouse of nutrition in small servings.
Frozen Buffalo Heart Nutrition
Protein Content
Buffalo heart is loaded with high-quality protein, providing essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. A single serving can offer over 20 grams of protein, making it ideal for fitness enthusiasts.
Richness in Vitamins
Vitamin B Complex
Buffalo heart is especially rich in B vitamins, including B12, B6, and niacin. These vitamins are crucial for energy metabolism and brain health.
Other Essential Vitamins
It also contains small amounts of vitamins A, E, and K, which support immune function, skin health, and blood clotting.
Mineral Content
Iron
The iron content in buffalo heart is exceptional, making it a great choice for individuals with iron deficiencies or anemia.
Zinc
Zinc helps with immune function and wound healing, and buffalo heart provides a healthy dose of this essential mineral.
Phosphorus
This mineral supports bone health and energy production.
Low in Fat
Unlike some other organ meats, buffalo heart is naturally low in fat, making it a great option for those watching their calorie intake.
Health Benefits of Consuming Frozen Buffalo Heart
Boosting Muscle Growth
Its high protein content aids in muscle repair and growth, especially after workouts.
Enhancing Energy Levels
With B vitamins and iron, buffalo heart supports energy production and combats fatigue.
Supporting Cardiovascular Health
Rich in Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), it may improve heart health and reduce oxidative stress.
Improving Iron Levels in the Body
For individuals with anemia or low iron levels, buffalo heart is a natural way to boost hemoglobin production.
Rich Source of Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and may help in preventing certain chronic diseases.
How to Incorporate Frozen Buffalo Heart into Your Diet
Different Ways to Prepare Frozen Buffalo Heart
Grilling
Grilling buffalo heart adds a smoky flavor and preserves its texture.
Sautéing
Quick sautéing with garlic and herbs brings out its natural flavor.
Stewing
Slow-cooked stews make buffalo heart tender and flavorful, perfect for hearty meals.
Pairing Suggestions
Pair it with root vegetables, leafy greens, or whole grains to create balanced meals.
Portion Size and Frequency
Start with small portions (3-4 ounces) once or twice a week to integrate it into your diet without overwhelming your palate.
Who Should Eat Frozen Buffalo Heart?
Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
Its high protein and nutrient content make it a perfect post-workout meal.
Individuals with Anemia
The iron-rich composition helps combat iron deficiency.
Those Seeking a High-Nutrient, Low-Fat Diet
For those managing weight or seeking nutrient density, buffalo heart is an excellent choice.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
Allergy Risks
Some individuals may be allergic to organ meats. It’s important to test tolerance before regular consumption.
Proper Handling and Cooking
To avoid foodborne illnesses, ensure the heart is properly cleaned, stored, and cooked.
Ethical and Environmental Concerns
Consider sourcing from sustainable and ethical farms to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
Frozen buffalo heart is a nutritional powerhouse that’s often overlooked. Packed with protein, vitamins, minerals, and low in fat, it supports overall health and wellness. Whether you’re looking to boost muscle growth, improve energy, or add variety to your meals, buffalo heart is worth trying.
FAQs
What does buffalo heart taste like?
Buffalo heart has a mild flavor, slightly gamier than beef, with a tender yet firm texture.
Can I feed buffalo heart to pets?
Yes, buffalo heart is a great source of nutrition for pets, especially dogs and cats, when cooked or served raw in appropriate portions.
How should frozen buffalo heart be stored?
Store it in airtight packaging in the freezer, and thaw it in the refrigerator before use.
Is frozen buffalo heart better than fresh?
Freezing preserves the nutrients and extends shelf life, making it just as nutritious as fresh buffalo heart.
Can buffalo heart help with weight loss?
Yes, its high protein and low-fat content make it a filling, low-calorie food that supports weight management.Frozen buffalo heart may not be the first thing that comes to mind when considering healthy food options, but this nutrient-packed organ meat deserves a spot in your diet. Whether you’re an athlete looking for high-quality protein or someone seeking a low-fat, nutrient-dense food, frozen buffalo heart is a hidden gem.
What is Frozen Buffalo Heart?
The buffalo heart is a lean, nutrient-dense organ meat from the water buffalo. When frozen, it retains its nutritional properties, making it convenient and long-lasting for storage.
Why Consider Frozen Buffalo Heart for Nutrition?
Organ meats like buffalo heart have been staples in traditional diets for centuries due to their rich nutrient content. Unlike muscle meat, organ meats are often higher in vitamins and minerals, offering a powerhouse of nutrition in small servings.
Nutritional Profile of Frozen Buffalo Heart
Protein Content
Buffalo heart is loaded with high-quality protein, providing essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. A single serving can offer over 20 grams of protein, making it ideal for fitness enthusiasts.
Richness in Vitamins
Vitamin B Complex
Buffalo heart is especially rich in B vitamins, including B12, B6, and niacin. These vitamins are crucial for energy metabolism and brain health.
Other Essential Vitamins
It also contains small amounts of vitamins A, E, and K, which support immune function, skin health, and blood clotting.
Mineral Content
Iron
The iron content in buffalo heart is exceptional, making it a great choice for individuals with iron deficiencies or anemia.
Zinc
Zinc helps with immune function and wound healing, and buffalo heart provides a healthy dose of this essential mineral.
Phosphorus
This mineral supports bone health and energy production.
Low in Fat
Unlike some other organ meats, buffalo heart is naturally low in fat, making it a great option for those watching their calorie intake.
Health Benefits of Consuming Frozen Buffalo Heart
Boosting Muscle Growth
Its high protein content aids in muscle repair and growth, especially after workouts.
Enhancing Energy Levels
With B vitamins and iron, buffalo heart supports energy production and combats fatigue.
Supporting Cardiovascular Health
Rich in Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), it may improve heart health and reduce oxidative stress.
Improving Iron Levels in the Body
For individuals with anemia or low iron levels, buffalo heart is a natural way to boost hemoglobin production.
Rich Source of Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and may help in preventing certain chronic diseases.
How to Incorporate Frozen Buffalo Heart into Your Diet
Different Ways to Prepare Frozen Buffalo Heart
Grilling
Grilling buffalo heart adds a smoky flavor and preserves its texture.
Sautéing
Quick sautéing with garlic and herbs brings out its natural flavor.
Stewing
Slow-cooked stews make buffalo heart tender and flavorful, perfect for hearty meals.
Pairing Suggestions
Pair it with root vegetables, leafy greens, or whole grains to create balanced meals.
Portion Size and Frequency
Start with small portions (3-4 ounces) once or twice a week to integrate it into your diet without overwhelming your palate.
Who Should Eat Frozen Buffalo Heart?
Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
Its high protein and nutrient content make it a perfect post-workout meal.
Individuals with Anemia
The iron-rich composition helps combat iron deficiency.
Those Seeking a High-Nutrient, Low-Fat Diet
For those managing weight or seeking nutrient density, buffalo heart is an excellent choice.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
Allergy Risks
Some individuals may be allergic to organ meats. It’s important to test tolerance before regular consumption.
Proper Handling and Cooking
To avoid foodborne illnesses, ensure the heart is properly cleaned, stored, and cooked.
Ethical and Environmental Concerns
Consider sourcing from sustainable and ethical farms to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
Frozen buffalo heart is a nutritional powerhouse that’s often overlooked. Packed with protein, vitamins, minerals, and low in fat, it supports overall health and wellness. Whether you’re looking to boost muscle growth, improve energy, or add variety to your meals, buffalo heart is worth trying.
FAQs
What does buffalo heart taste like?
Buffalo heart has a mild flavor, slightly gamier than beef, with a tender yet firm texture.
Can I feed buffalo heart to pets?
Yes, buffalo heart is a great source of nutrition for pets, especially dogs and cats, when cooked or served raw in appropriate portions.
How should frozen buffalo heart be stored?
Store it in airtight packaging in the freezer, and thaw it in the refrigerator before use.
Is frozen buffalo heart better than fresh?
Freezing preserves the nutrients and extends shelf life, making it just as nutritious as fresh buffalo heart.
Can buffalo heart help with weight loss?
Yes, its high protein and low-fat content make it a filling, low-calorie food that supports weight management.

